Magnesium involved in building and maintaining strong bones and also plays a role in other bodily functions. In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about calcium, from its essentials to the potential effects of calcium deficiency on health. We will also explore calcium-rich food sources and the daily requirements for calcium.
The Essence of Calcium
Calcium is a mineral that is important for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Besides its role in bone health, calcium also participates in muscle contraction, nerve function, and blood clotting. It is essential for overall health and the proper functioning of various systems.
Calcium: The Building Block of Strong Bones
One of the key functions of calcium is to support the health of our bones. Calcium is involved in building and maintaining bone mass, which can strengthen bones and may help reduce the risk of fractures. Regular intake of sufficient calcium is particularly important during childhood and adolescence when bones are developing.
Calcium Absorption: How Does It Work in Your Body?
Calcium is absorbed in the body through the intestines. Its absorption is influenced by various factors, including the presence of vitamin D, magnesium, and certain hormones. For instance, vitamin D assists the body in absorbing calcium from food or supplements effectively. It is important to ensure adequate intake of these nutrients to optimize calcium absorption.
Calcium-Rich Foods
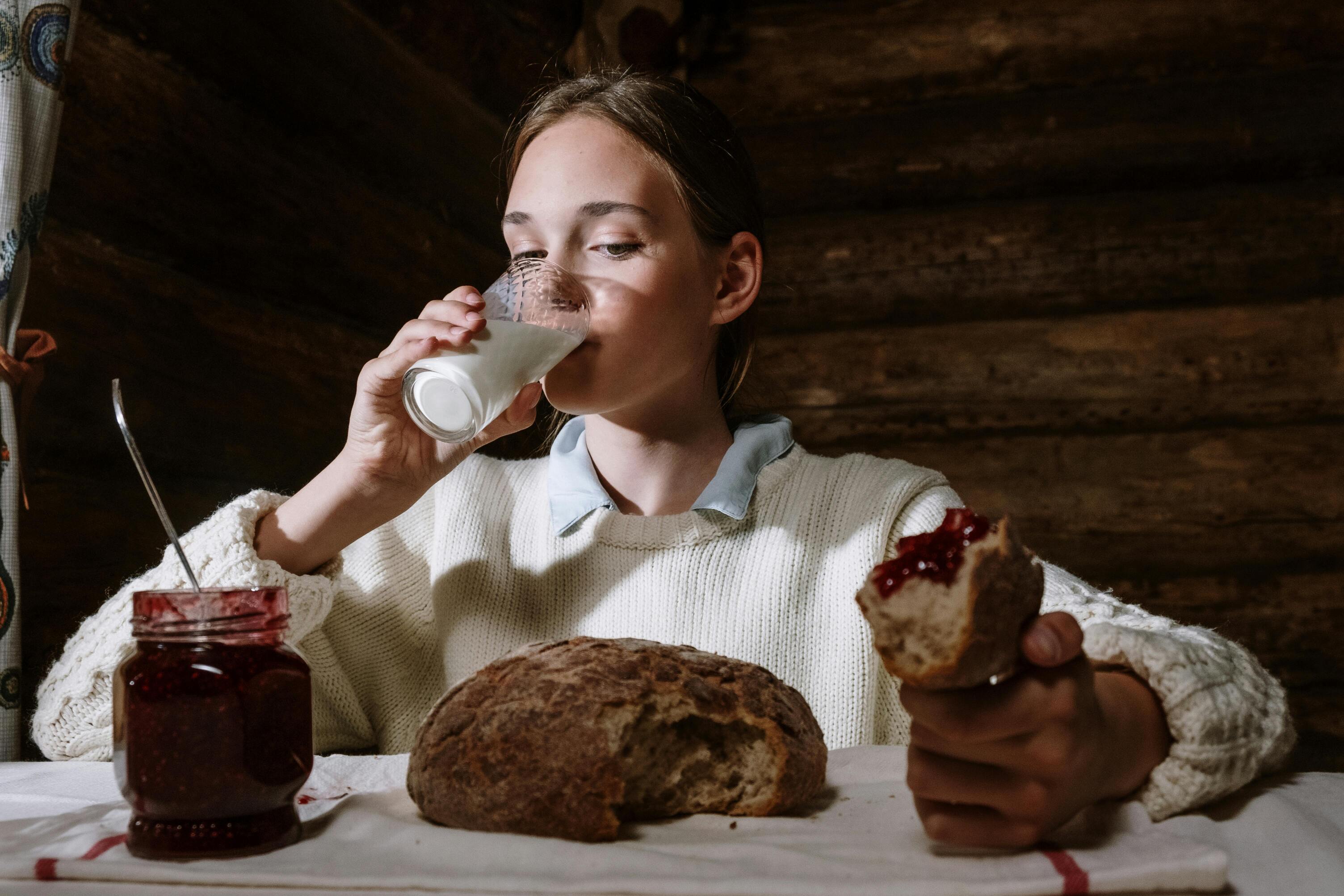
There are various calcium-rich food sources that you can include in your diet. Dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, are well-known sources of calcium. Other good sources include green leafy vegetables like kale and spinach, nuts, seeds, legumes, and certain fish like sardines and salmon. It’s important to have a varied diet that includes these foods to help meet your calcium needs.
What Does Calcium Do for Your Body?
As mentioned earlier, calcium serves several functions in the body. Besides being important for bone health, it also plays a role in muscle contraction and nerve function. Calcium is involved in transmitting nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Additionally, it helps regulate heart rate and blood pressure. Calcium also has a role in blood clotting, which is essential for the body’s healing process.
How Much Calcium Per Day?
The daily calcium requirement varies by age group. For children aged 1-3 years, the recommended intake is about 700 mg per day. For children aged 4-8 years, this is 1000 mg per day. Teenagers aged 9-18 years need slightly more calcium, approximately 1300 mg per day. For adults aged 19-50 years, the recommended intake is 1000 mg per day, and for adults over 51 years, it is 1200 mg per day. Pregnant women also have a slightly higher calcium requirement, around 1000 mg per day.
The Impact of Calcium Deficiency on Health
A calcium deficiency can lead to various health concerns. It may increase the risk of conditions like osteoporosis, where bones become more fragile. A lack of calcium can also contribute to muscle cramps and general fatigue. It is important to meet your calcium needs to support overall health.
The Risks of Excessive Calcium Intake
While calcium is important for the body, it is possible to consume too much. Excessive calcium intake may lead to kidney stones and can interfere with the absorption of other minerals, such as iron and zinc. It is essential to stay within the recommended limits to avoid potential health risks.
The Acceptable Upper Limit of Calcium Consumption
The acceptable upper limit of calcium consumption for adults is set at 2500 mg per day. It’s important not to exceed this limit to help prevent negative health effects. Balancing your calcium intake is wise, and consulting a dietitian or nutritionist can be beneficial if you have questions about your dietary needs.